Bottleneck Architectures
Bottleneck Design
As we discovered in the previous section that regardless of the complexity, the pattern of dimensions increase + identity shortcuts performs the best. It is reasonable to assume that the same pattern will work for deeper networks as well.
The author introduced the bottleneck design. The left of the following picture is a normal residual network, there is no dimension change included. The right is the bottleneck design.
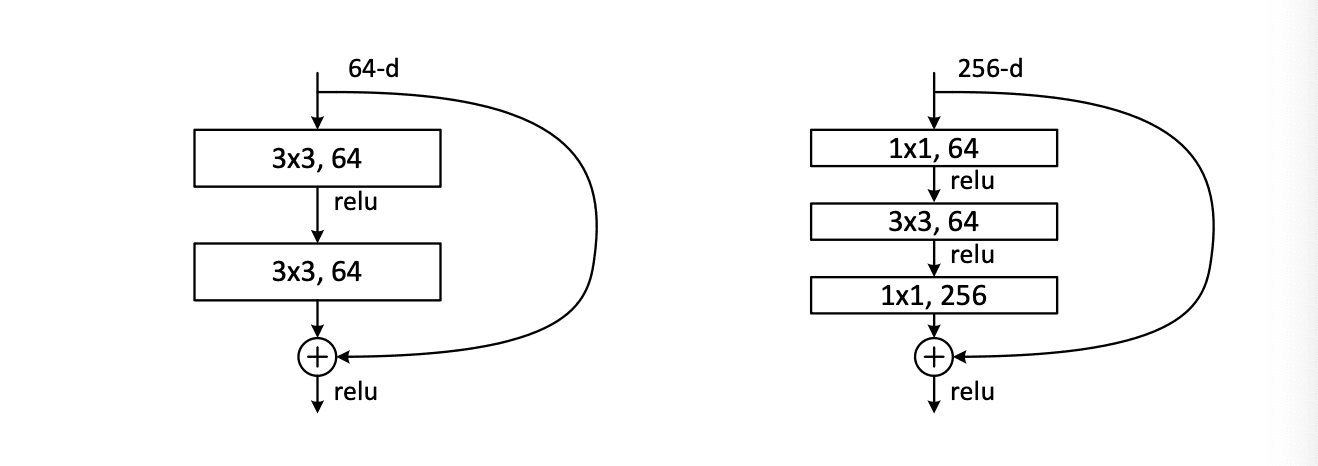
For each residual function , we use a stack of 3 layers instead of 2. The three layers are 1×1, 3×3, and 1×1 convolutions, where the 1×1 layers are responsible for reducing and then increasing (restoring) dimensions, leaving the 3×3 layer a bottleneck with smaller input/output dimensions.
One important feature is that the bottleneck design is parameter-free. If the identity shortcut is replaced with projection, the complexity and size of the model will be doubled. So identity shortcuts lead to more efficient models for the bottleneck designs.
Comparison
Four different ResNet are used in this experiment: ResNet-34, ResNet-50, ResNet-101, and ResNet-152.
- ResNet-50: replace each 2-layer block in the 34-layer net with the 3-layer bottleneck block, resulting in a 50-layer ResNet.
- ResNet-101 and ResNet-152: We construct 101-layer and 152-layer ResNets by using more 3-layer blocks
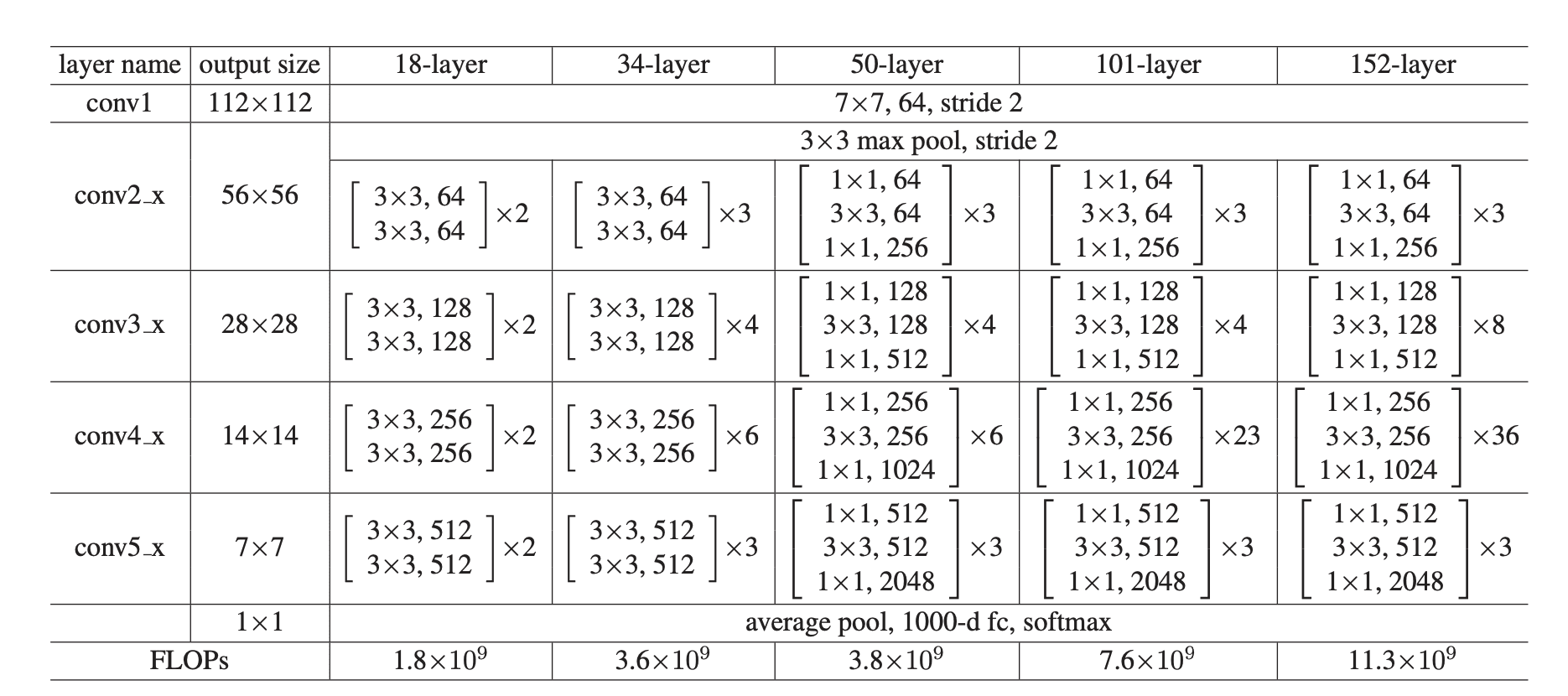
The experiment results are shown below.
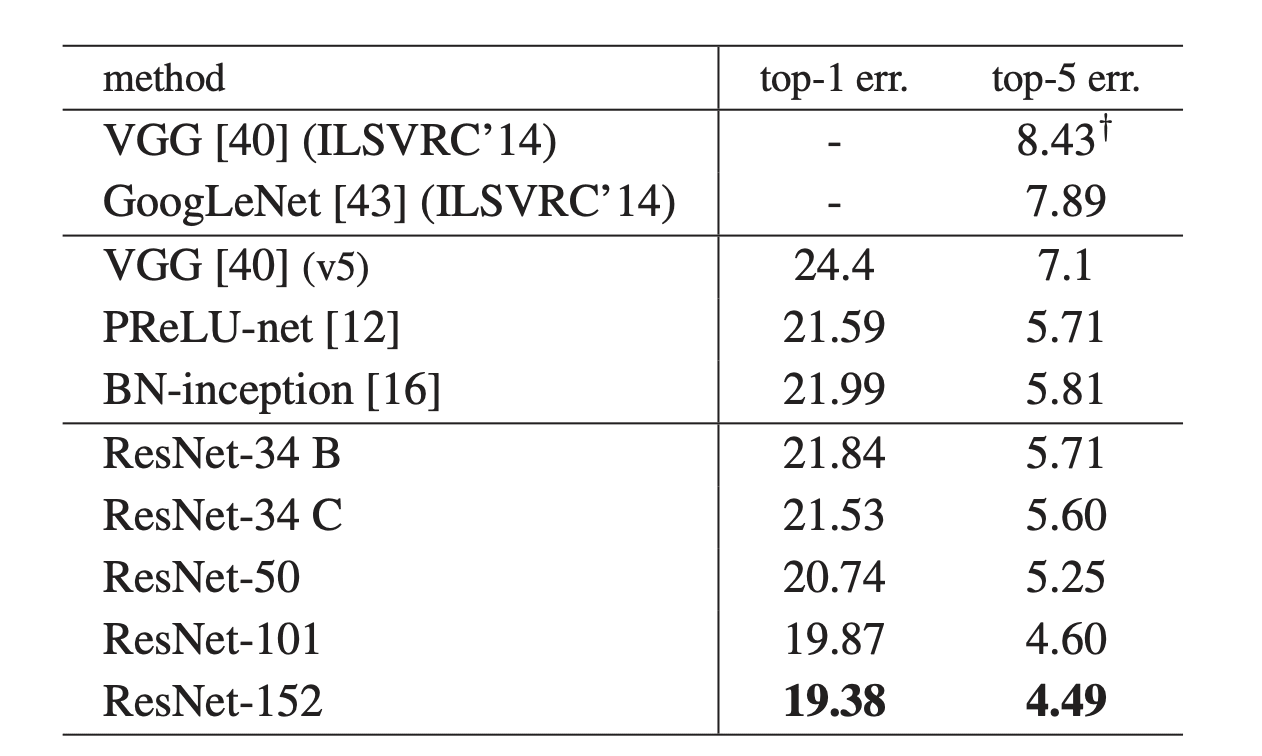
ResNet is the best among all the models. And among the resnet models, we can see the error drop as the model gets deeper with the bottleneck design.